
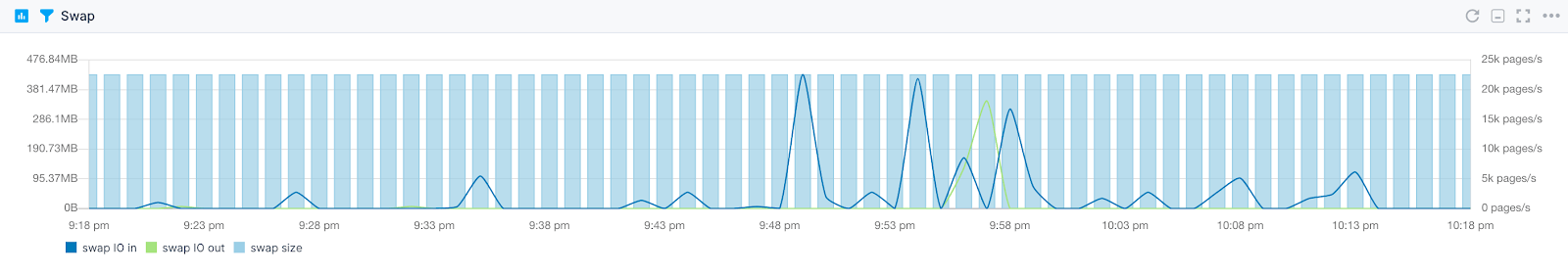
Watch how big the various memory spaces get over time (hours or days), as you run various common DSpace tasks that put load on memory, including indexing, reindexing, importing items into the oai index etc. Note how much memory Tomcat is using upon startup and use a slightly higher value than that for the -Xms parameter (initial Java heap size). In the " System Information" tab, go to the " Memory utilization" menu.
#Solr jvm memory monitor password#
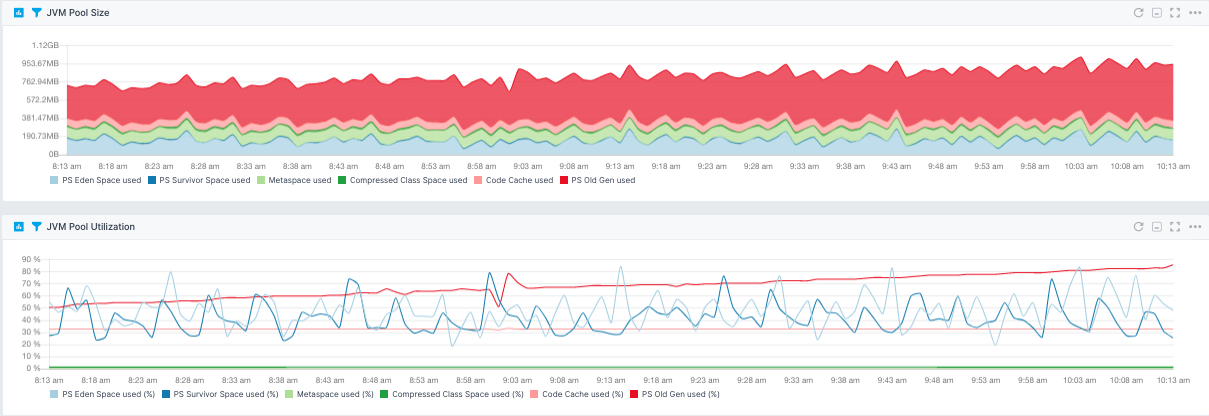
The G1GC garbage collector is currently preferred when using a JVM that supports it (Java 9 and later).When heaps grow to larger sizes, it is imperative to test extensively before going to production. 8-16Gb is quite common, and larger heaps are sometimes used. The heap allocated should be as small as possible while maintaining good performance.Therefore, as much memory as possible should be left for the operating system to use for this purpose. Lucene/Solr makes extensive use of MMapDirectory, which uses RAM not reserved for the JVM for most of the Lucene index.Running Solr with too little "headroom" allocated for the heap can cause excessive resources to be consumed by continual GC.There are several points to keep in mind: This will show the absolute minimum amount of memory required adding 25-50% "headroom" is a reasonable starting point. Also you can attach jconsole (distributed with most Java runtimes) to check memory consumption as Solr is running. There are various tools that help analyze these logs and, in particular, show the amount of memory used after GC has completed ( GCViewer and GCEasy are two). The best way to determine the correct size is to analyze the garbage collection (GC) logs located in your logs directory. Heap size is critical and unfortunately there is no "one size fits all" solution, you must test with your data and your application. Setting these two options to the same value is a common practice. The most important JVM configuration settings control the heap allocated to the JVM: -Xms, which sets the initial size of the JVM’s memory heap, and -Xmx, which sets the maximum size of the heap.
The following sections contain a few tips that may be helpful when the defaults are not optimal for your situation.įor more general information about improving Solr performance, see Solr Performance Factors in the Solr Wiki. Luckily, most modern JVMs are quite good at making the best use of available resources with default settings.
#Solr jvm memory monitor full#
Optimizing the JVM can be a key factor in getting the most from your Solr installation.Ĭonfiguring your JVM is a complex topic and a full discussion is beyond the scope of this document.
#Solr jvm memory monitor how to#



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
